Hardware Hinge Inspection Process
1. Purpose
To ensure piano hinges meet quality standards and specifications before acceptance or installation.
2. Scope
Applies to all incoming piano hinges (continuous hinges) for furniture, doors, cabinets, or industrial applications.
3. Inspection Tools & Equipment
Caliper/Micrometer
Ruler/Tape Measure
Hardness Tester (if required)
Visual Inspection Light

Sample Drawing/Specification Sheet
4. Inspection Steps
4.1 Documentation Check
Verify purchase order, material certificates (e.g., stainless steel, brass, aluminum), and compliance with standards (e.g., ASTM, EN).
4.2 Visual Inspection
Surface Quality: No cracks, burrs, rust, or uneven plating/painting.
Finish: Consistent color, no peeling, scratches, or discoloration.
Markings: Check for manufacturer logo, material grade (e.g., 304 SS), and size markings.

4.3 Dimensional Inspection
Length: Match ordered dimensions (±1mm tolerance unless specified).
Width & Thickness: Confirm leaf width and thickness per specs.
Hole Spacing: Verify uniform hole spacing and diameter.
Pin Diameter: Measure hinge pin for proper fit.
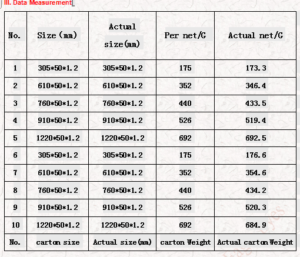

4.4 Functional Testing
Smooth Operation: Rotate hinge 180°—must move freely without sticking.
Alignment: Leaves must align perfectly when open/closed.
Load Test (if required): Test with weight to ensure no deformation.
4.5 Material Verification
Hardness Test (if applicable): Use Rockwell or Vickers tester.
Magnet Test (for stainless steel): Austenitic SS should be non-magnetic.
4.6 Corrosion Check
For rust-resistant materials (e.g., SS 316), inspect for pitting or salt-spray test reports.
5. Defect Classification
Critical Defect: Broken pin, incorrect material—immediate rejection.
Major Defect: Poor finish, misaligned holes—requires supplier approval.
Minor Defect: Slight scratches—may accept with waiver.