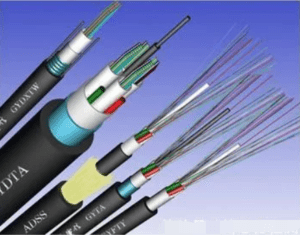

Optical cable is to meet the optical, mechanical or environmental performance specifications and manufacturing, mainly composed of optical fiber and plastic protection sleeve and plastic sheath, is a certain number of optical fiber in accordance with a certain way to form the cable core, outer sheath, some also covered with outer sheath, to achieve optical signal transmission of a communication line.
Basic structure:
it is composed of cable core, reinforcing steel wire, filling material and sheath, and waterproof layer, buffer layer, insulating metal wire and other components as required.
The cable is composed of three parts: strengthening core, cable core, sheath and outer sheath. There are two types of cable core structure: single core and multi-core. Single core type has two kinds of enrichment type and bundle type; The multicore type has two types: strip type and unit type. There are two kinds of outer protective layers, metal armored and non-armored.
Detection range:
Submarine optical cable, outdoor optical cable, flame retardant optical cable for mining, communication optical cable, fusion optical cable, overhead optical cable, power cable, directly buried optical cable, etc.
Test Items:
Attenuation testing, welding strength test, water permeability test, tensile test, bending test repeatedly, the tensile test, torsional strength test, dropping collision detection, plug 200 times durability test, bending test, the locking force test, static lateral tensile testing, load transmission performance testing, flame retardant, high temperature resistance test, electric performance test, tensile test after aging, High temperature pressure detection, thermal impact detection, thermal extension detection, hydroscopicity detection, thermal shrinkage strength detection, low temperature resistance detection, water spray detection, conductor DC resistance detection, electric spark detection, tensile strength detection, elongation at break detection, low temperature winding detection, etc.
Test criteria:
Communications optical cables — Part 1: General principles
GB/T 31248-2014 Test method for flame spread, heat release and smoke generation characteristics of cables or optical cables under fire conditions
GB/T 29199-2012 Test method for rodent proof performance of optical cables
GB/T 24202-2009 fiber optic cable reinforced carbon steel wire
GB/T 2951.12-2008 General test method for insulation and sheath materials for cables and optical cables — Part 12: General test method — thermal ageing test method
GB/T 2951.14-2008 Cables and optical cables — General test methods for insulation and sheath materials — Part 14: General test methods — low temperature testGB/T 2951.31-2008 General test methods for insulation and sheath materials for cables and optical cables — Part 31: Special test method for polyvinyl chloride mixtures — high temperature and pressure test — resistance to cracking test
GB/T 2951.41-2008 Cables and optical cables — General test methods for insulation and sheath materials — Part 41: Special test method for polyethylene and polypropylene mixtures — Resistance to environmental stress cracking test — Melt index measurement method — Determination of carbon black and/or mineral filler content in polyethylene by direct combustion method — Determination of carbon black content by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) — microscopic evaluation of carbon black dispersion in polyethylene
GB/T 18380.11-2008 Cables and optical cables — Fire tests under flame conditions — Part 11: Vertical flame spread test apparatus for single insulated wire and cable
GB/T 18380.21-2008 Cables and optical cables — Fire tests under flame conditions — Part 21: Vertical flame spread test apparatus for single insulated thin wire and cable